

These bytes are repeated by the Slave device in the response, since the responses of the Slave device may not always be received in the same order as the requests. Transaction Identifier: 2 bytes are set by the Master to uniquely identify each request.

We drop the address of the SlaveID device and the CRC checksum and get the PDU: 03 006B 0003Īt the beginning of the received PDU message, a new 7-byte header is added, which is called MBAP Header (Modbus Application Header).
The number of required registers (reading 3 registers from 40108 to 40110)
#Packet sender tcp response data code
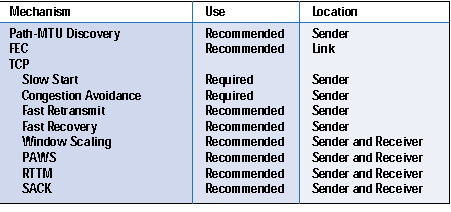
The following is an example of a Modbus RTU request for obtaining the AI value of the holding registers from registers # 40108 to 40110 with the address of the device 17.įunction Code (read Analog Output Holding Registers)Īddress of the first register (40108-40001 = 107 = 6B hex) The Modbus TCP command consists of a portion of the Modbus RTU message and a special header.įrom the Modbus RTU message, the SlaveID address at the beginning and the CRC checksum at the end are removed, which forms the PDU, the Protocol Data Unit. The interface is an Ethernet network, the data transfer protocol is TCP / IP.īack to contents Description of the Modbus TCP protocol 20 when using the most common subnet mask 255.255.255.0. Typically, devices are on the same subnet, where IP addresses differ by the last two digit 192.168.1. In an Ethernet network, the device address is its IP address. Equipment with Modbus TCP support Where to send a Modbus TCP command?.Programs for working with the Modbus TCP protocol.How do I send a Modbus TCP command to write multiple analog outputs? Command 0x10.How do I send a Modbus TCP command to write multiple discrete pins? Command 0x0F.How do I send a Modbus TCP command to record analog output? Command 0x06.How do I send a Modbus TCP command to write discrete output? Command 0x05.
#Packet sender tcp response data how to


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
